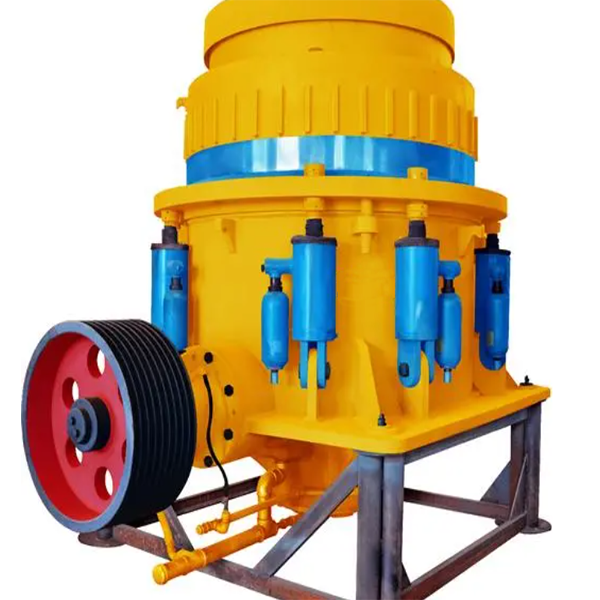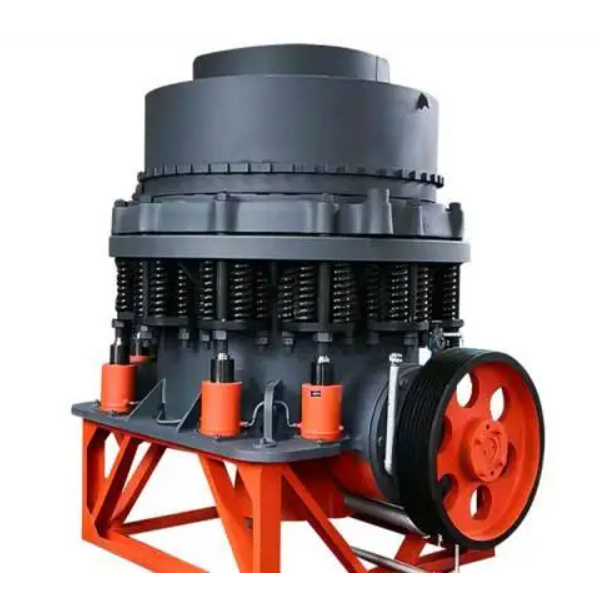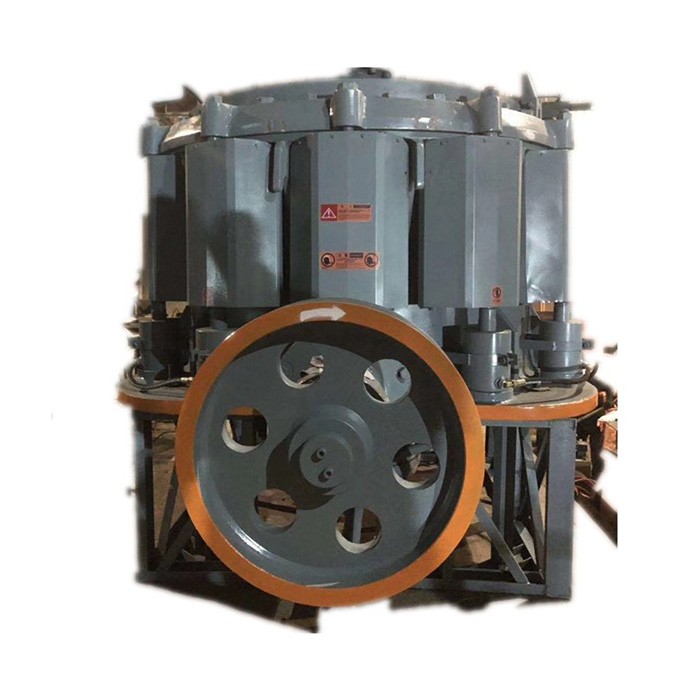
Detailed Introduction to CH Series Cone Crusher
1. Overview and Application of CH Series Cone Crusher
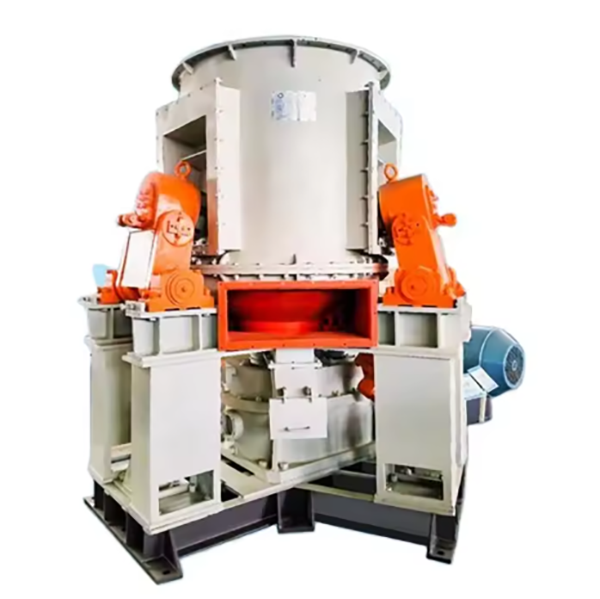
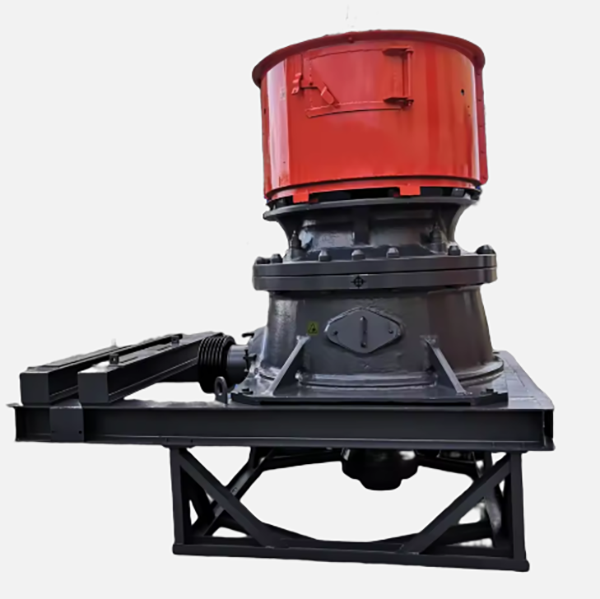
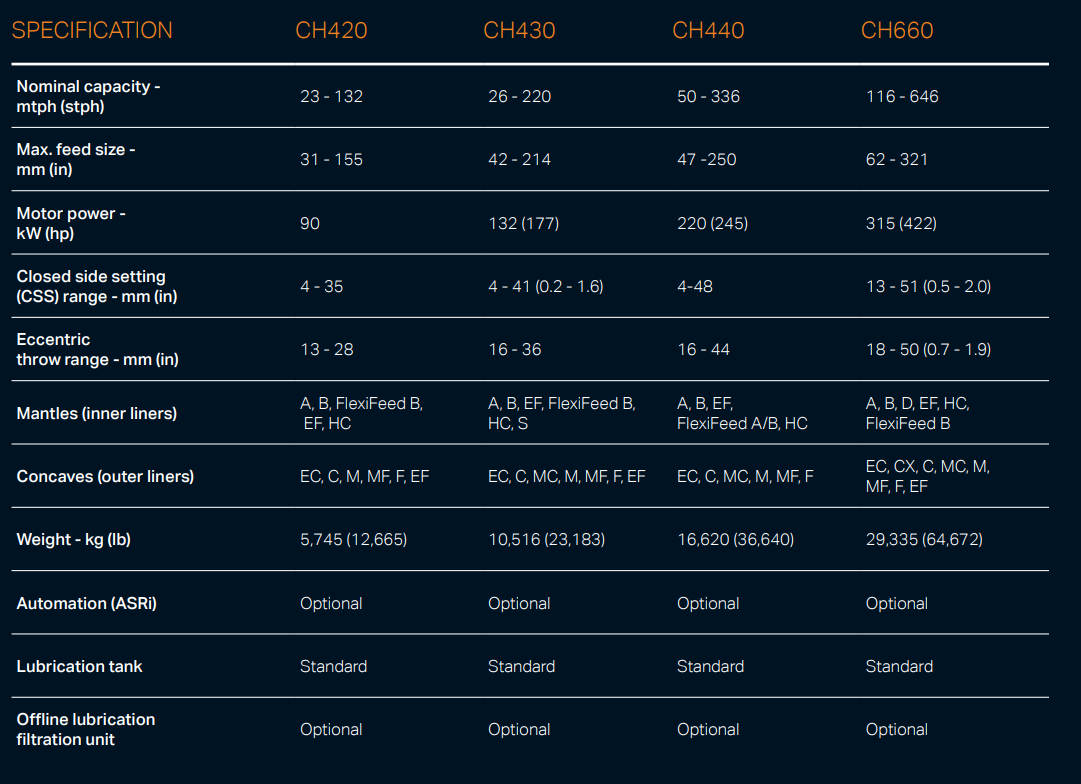
The CH series cone crusher is a high-performance medium-to-fine crushing equipment developed for hard and abrasive materials, widely used in mining, aggregate production, and metallurgical industries. It integrates advanced technologies such as optimized cavity design, hydraulic adjustment, and intelligent control, featuring high crushing efficiency (up to 2000 t/h), excellent product cubicity (≥85%), and strong adaptability to materials like granite, basalt, and ore.
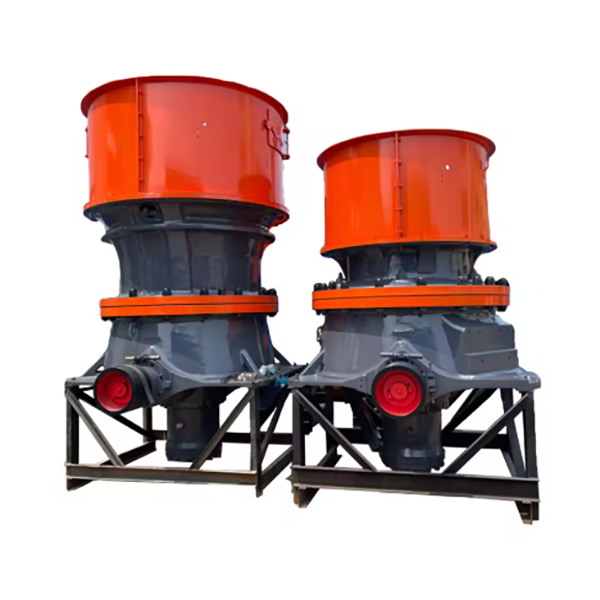
Its working principle is based on lamination crushing: the motor drives the eccentric shaft sleeve to rotate, causing the moving cone to swing periodically. Materials are squeezed, bent, and impacted between the moving cone and fixed cone, gradually crushed into uniform particles and discharged through the adjustable discharge port. The series includes models such as CH430, CH660, and CH890, covering different processing capacities to meet diverse production needs.
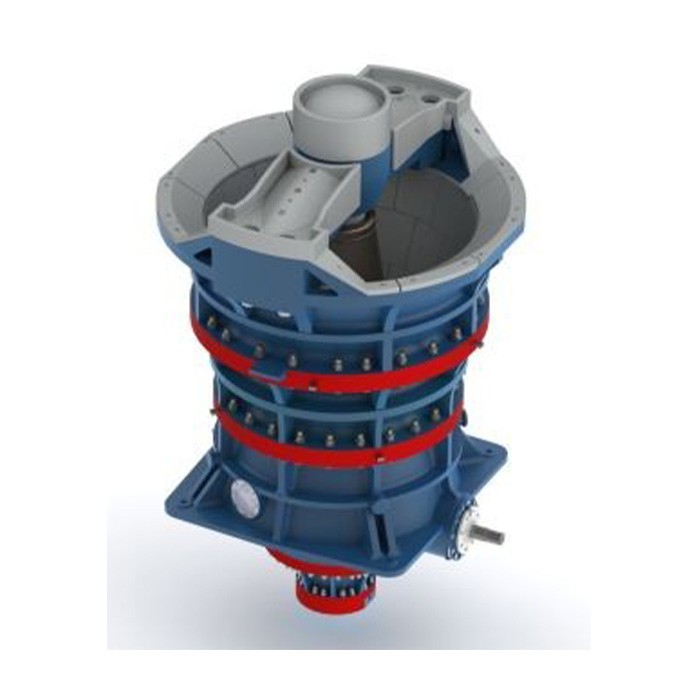
2. Composition and Structure of CH Series Cone Crusher
The CH series cone crusher consists of core assemblies with precise coordination, ensuring stable and efficient operation:
2.1 Main Frame Assembly
Lower Frame: A heavy-duty cast steel (ZG35CrMo) base housing the eccentric shaft sleeve, main shaft bearing, and hydraulic cylinders. It is bolted to the foundation with anchor bolts (M30–M60) and features internal oil passages for lubrication.
2.2 Crushing Assembly
Moving Cone: Comprises a forged 42CrMo cone body and a high-chromium cast iron (Cr20) liner. The cone body has a spherical bottom fitting the main shaft’s spherical bearing, enabling flexible swing. The liner is fixed via zinc alloy casting to ensure tight contact, with a wear-resistant layer thickness of 30–80 mm.
Fixed Cone (Concave): A segmented annular liner (3–6 segments) made of Cr20 or ZGMn13, mounted on the upper frame. Each segment’s cavity profile (angle 18°–25°) is optimized for specific particle size requirements, with interlocking structures to prevent material leakage.
2.3 Transmission and Drive System
Eccentric Shaft Sleeve: A cast steel (ZG35CrMo) sleeve with an eccentricity of 10–30 mm, driving the main shaft’s oscillation. It is equipped with a large bevel gear (20CrMnTi, carburized and quenched) and mounted on spherical roller bearings.
2.4 Hydraulic and Control System
Safety System: Overload protection via pressure relief valves. When uncrushable materials enter, cylinders retract to expand the discharge port, expel foreign matter, and reset automatically.
Intelligent Control Cabinet: PLC-based system monitoring temperature, pressure, and power, with remote operation and fault diagnosis functions.
2.5 Lubrication and Dustproof System
Thin Oil Lubrication: An independent system with dual pumps, coolers, and filters, circulating ISO VG 46 oil to bearings and gears at 0.2–0.4 MPa, maintaining temperature <55°C.
3. Casting Processes for Key Components
3.1 Frame (ZG270-500/ZG35CrMo)
3.2 Eccentric Shaft Sleeve (ZG35CrMo)
3.3 Moving Cone Body (42CrMo Forging)
4. Machining Processes
4.1 Frame Machining
4.2 Eccentric Shaft Sleeve Machining
4.3 Moving Cone Machining
5. Quality Control Processes
6. Installation Process
The CH series cone crusher, through precise manufacturing and strict quality control, delivers reliable performance in large-scale crushing operations, ensuring high efficiency and product quality












