Vibrating Screens wire mesh
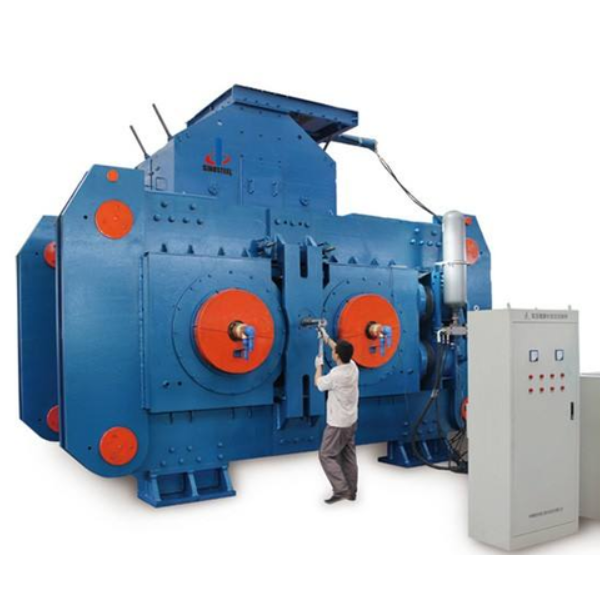
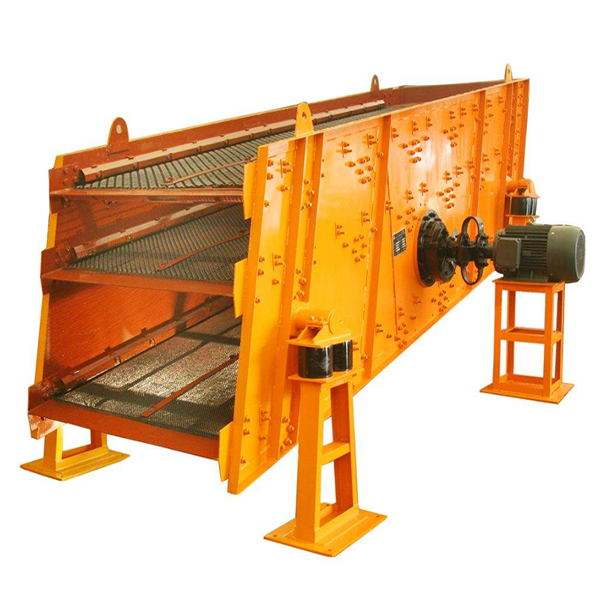
Vibrating screens wire mesh, a key component in screening equipment, classifies bulk materials (ore, aggregate, etc.) by particle size via vibration, with 85–95% efficiency. It withstands high-frequency vibration (800–3000 rpm) and abrasion, requiring high tensile strength and wear resistance.
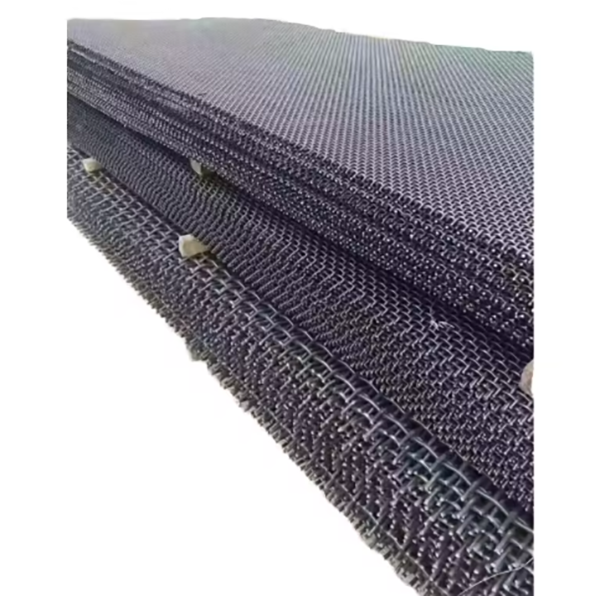
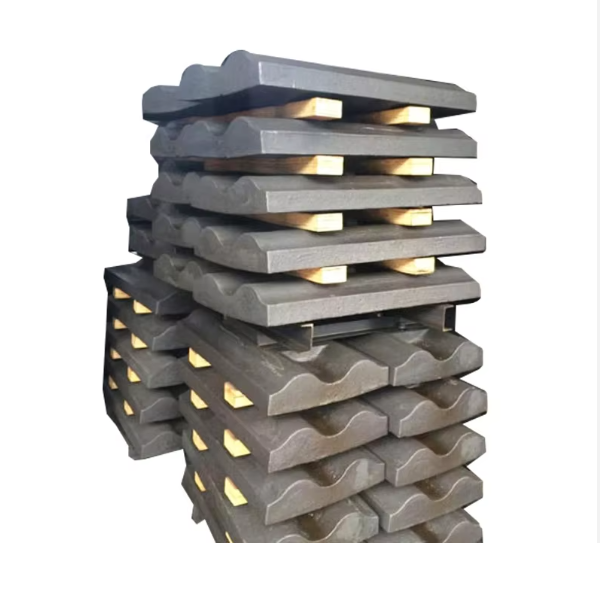
Composed of warp/weft wires (materials: high-carbon steel, stainless steel), mesh openings (0.1–100 mm, square/rectangular/hexagonal), and edge reinforcement, it has structural types: woven (plain/twill/Dutch weaves), welded (rigid welded intersections), and perforated plate (punched steel plates).
Manufacturing processes vary by type: woven mesh involves wire drawing, straightening, weaving, and edge treatment; welded mesh uses wire preparation, grid alignment, resistance welding, and surface treatment; perforated mesh requires plate cutting, punching, and deburring. Finishing includes galvanizing, polishing, or coating.
Quality control covers material testing (tensile strength, composition), dimensional checks (opening size, flatness), structural tests (weld strength, abrasion resistance), and performance validation (screening efficiency, vibration fatigue).
Installation involves frame preparation, mesh positioning, fixing (bolts/wedge bars), tension adjustment (10–20 kN/m), and sealing/testing to ensure stable operation. This mesh is vital for efficient material classification in mining, construction, and metallurgy.
More